Current EU Food Safety Regulatory Landscape
The European Union maintains stringent food safety standards, with HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) as the cornerstone of compliance 2. For Malaysian food manufacturers, understanding these requirements is crucial for accessing the EU’s €1.2 trillion food and drink industry 3 and the broader €18 trillion Single Market with 450 million consumers 4.
The EU’s food safety framework has significant updates in 2025, including Regulation (EU) 2025/351 introducing enhanced safety requirements for food contact materials 5. Additionally, the European Commission’s comprehensive Health and Food Audits programme targets 259 planned controls across member states and third countries 6, emphasising the EU’s commitment to food safety excellence.
HACCP implementation has been mandatory for all food businesses placing products on the EU market since January 1, 2006, under EU Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 7. The updated Commission Notice 2022/C 355/01 provides enhanced guidance on food safety management systems, highlighting the introduction of allergen control and food safety culture as requirements in Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 by Regulation (EU) 2021/382 8.
The Five Critical HACCP Requirements
1. Mandatory HACCP-Based Food Safety Management System
Every food business operator must implement and maintain procedures based on HACCP principles 9. This fundamental requirement, established under Article 5 of Regulation (EC) 852/2004, encompasses:
- Seven core HACCP principles covering hazard analysis, critical control point identification, critical limits establishment, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and documentation 10.
- Comprehensive coverage of biological, chemical, and physical hazards throughout all food chain stages 11.
- Regular validation and verification will, in a number of cases, require sampling and testing for microbiological or chemical hazards” 12.
The European Commission states that HACCP focuses on prevention rather than relying mainly on end-point testing and is a system of food safety assurance based on the prevention of food and feed safety problems 13.
2. Critical Control Points (CCPs) Implementation
Identification and effective control of Critical Control Points remains central to EU compliance 14. The updated guidance emphasises:
- Systematic hazard analysis: at each process step using decision tree methodology 15.
- Establishment of measurable critical limits: that separate acceptable from unacceptable conditions 16.
- Continuous monitoring procedures: providing real-time feedback on CCP status 17.
- Immediate corrective actions: when critical limits are exceeded, with documented procedures for product disposition 18.
The EU’s approach recognises that not every control point is critical—companies must focus on points where control is essential to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to acceptable levels 19.
3. Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) and Good Hygiene Practices
Prerequisite programs form the foundation upon which HACCP systems are built 20. The 2022 Commission Notice emphasises the critical role of PRPs, including:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): covering facility design, equipment maintenance, and operational procedures 21.
- Cleaning and Sanitation: with validated procedures and verification systems 22.
- Pest Control: preventing contamination throughout the facility 23.
- Staff Hygiene and Training: ensuring competent personnel at all levels 24.
- Supplier Verification: ensuring ingredient and packaging material safety 25.
These programs must be effectively implemented before HACCP principles can be successfully applied 30.
4. Documentation and Record-Keeping Systems
Comprehensive documentation serves as the backbone of HACCP compliance 31. EU requirements mandate:
- HACCP Plan Documentation: including hazard analysis, CCP determination, and control measures 32.
- Monitoring Records: demonstrating continuous compliance with critical limits 33.
- Corrective Action Documentation: showing immediate response to deviations and preventive measures 34.
- Verification Reports: confirming system effectiveness and scientific validity 35.
- Training Records: demonstrating staff competency and ongoing education 36.
Documentation must be readily available for inspection and demonstrate the system’s effectiveness in ensuring food safety 37.
5. Food Safety Culture and Management Commitment
The 2021 amendment to Regulation (EC) 852/2004 introduced mandatory food safety culture requirements 38. This involves:
- Management Commitment through formal food safety policies and resource allocation.
- Management Reviews of system performance and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Staff Competency ensuring personnel understand their food safety responsibilities.
- Open Communication encouraging reporting of food safety concerns without fear of reprisal.
- Continuous Improvement adapting to new risks, technologies, and regulatory requirements.
Management must demonstrate active leadership in food safety rather than delegating responsibility solely to quality assurance teams.
Malaysian Manufacturer Compliance Gaps
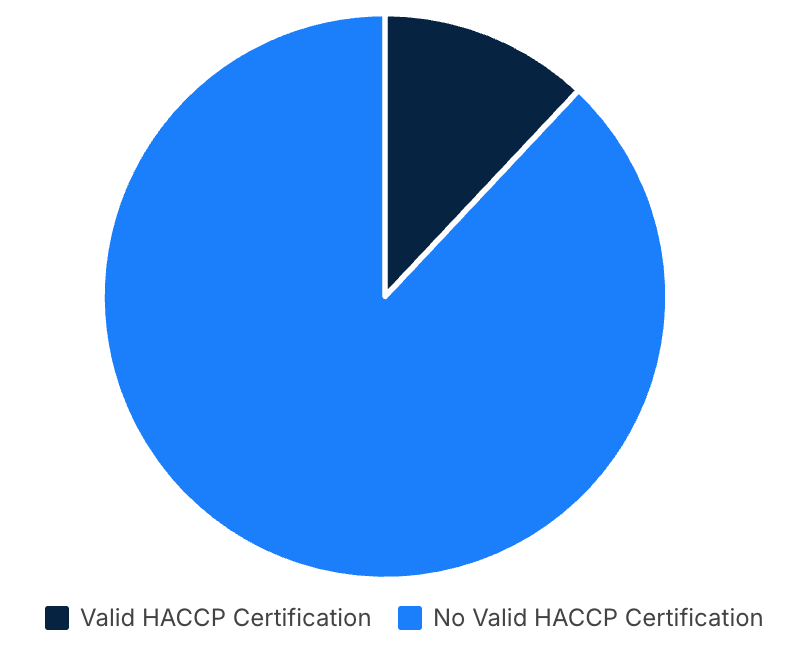
Current analysis reveals significant challenges for Malaysian manufacturers seeking EU market access. While Malaysia has approximately 6,000 food SMEs in its manufacturing sector 39, official Ministry of Health data from 2021 shows that of the 820 companies that have achieved HACCP certification, only 691 still maintain valid certification 40. This indicates that fewer than 12% of Malaysian food SMEs currently hold valid HACCP certification, representing a critical compliance gap of over 88% for EU market access requirements.
The Four Key Compliance Challenges
1. Documentation Standards
Malaysia’s MS1480 standard is fully aligned with Codex Alimentarius principles and implements the seven core HACCP principles as confirmed by SIRIM QAS International. However, Malaysian manufacturers face a significant documentation gap when seeking EU market access, as the European Commission’s Notice 2022/C 355/01 requires substantially more comprehensive documentation spanning 58 pages of detailed requirements. These EU requirements include extensive validation and verification procedures, detailed monitoring records, and comprehensive food safety culture documentation that substantially exceed the basic Codex implementation found in MS1480 certification.
2. Traceability Systems
Malaysian manufacturers face significant traceability challenges for EU market access. Academic research confirms that traceability and recall programs in Malaysia are still in early development stages, with only 52.9% of participants having implemented or showing interest in traceability systems. This contrasts with EU regulations that require complete supply chain transparency and plot-level traceability capabilities under EUDR and other regulations. Malaysian agro-food SMEs demonstrate low adoption intention for traceability systems and face challenges in adopting technological advances due to weak technological infrastructure and limited utilisation of information technologies.
3. Technical Expertise
Malaysian food SMEs face a severe shortage of qualified HACCP professionals, creating significant compliance challenges. Official research identifies lack of manpower and inadequate auditor skills as primary barriers, with manpower shortages directly causing certification delays.
The impact is quantified by academic studies showing that fewer than 500 out of 6,000 Malaysian food SMEs comply with HACCP and GMP standards. Contributing factors include high implementation costs, language barriers, and insufficient knowledge of HACCP importance, leading many SMEs to implement basic rather than comprehensive food safety systems, often without proper facility design considerations.
4. Audit Readiness
Many Malaysian manufacturers remain unprepared for the stringent HACCP audit requirements of European certification bodies and competent authorities. Research confirms that Malaysian food manufacturers face significant audit preparation challenges, including insufficient technical expertise among local auditors, gaps in comprehensive documentation systems, and limited experience with European audit standards.
The EU’s competent authorities require rigorous audit procedures under Regulation (EU) 2017/625 and Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627, including detailed verification of HACCP implementation, unannounced audits, and comprehensive documentation review. Malaysian certification bodies acknowledge the need for enhanced auditor qualifications and training to meet European standards, with the Department of Standards Malaysia requiring auditors to perform a minimum of five audits annually to maintain qualification.
The audit readiness gap is further evidenced by the low HACCP certification rate among Malaysian food SMEs and the challenges in meeting European certification body requirements for comprehensive food safety management systems.
Step-by-Step Compliance Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
- Management Commitment: Secure visible leadership support through formal policy establishment and resource allocation. Designate a qualified HACCP coordinator with authority to implement necessary changes.
- Team Formation: Assemble a multidisciplinary HACCP team including production, quality assurance, maintenance, and senior management representatives. Ensure team members receive appropriate HACCP training.
- Gap Assessment: Conduct comprehensive analysis comparing current practices with EU requirements. Prioritise improvement areas based on compliance criticality and implementation complexity.
Phase 2: System Implementation (Months 4-8)
- Prerequisite Programs: Establish robust PRPs including GMP procedures, cleaning protocols, pest control systems, and supplier verification programs meeting EU standards.
- Hazard Analysis: Conduct systematic hazard identification covering biological, chemical, and physical risks throughout the production process. Document control measures for each identified hazard.
- CCP Determination: Apply decision tree methodology to identify true critical control points. Establish measurable critical limits with validated monitoring procedures and defined corrective actions.
Phase 3: Validation and Training (Months 9-12)
- System Validation: Confirm that critical limits effectively control identified hazards through scientific validation studies. Calibrate monitoring equipment and verify measurement accuracy.
- Staff Training: Implement comprehensive training programs covering HACCP principles, specific procedures, and food safety culture requirements. Assess competency and maintain training records.
- Internal Auditing: Establish internal audit capabilities to continuously verify system effectiveness and identify improvement opportunities.
Phase 4: Certification and EU Verification (Months 13-15)
- External Certification: Engage accredited certification bodies recognised by European competent authorities. Successfully complete Stage 1 (documentation) and Stage 2 (implementation) audits.
- EU Compliance Verification: Ensure full alignment with Regulation (EC) 852/2004 and Commission Notice 2022/C 355/01 requirements. Verify traceability capabilities and food safety culture implementation.
Phase 5: Continuous Improvement (Ongoing)
- Ongoing Monitoring: Maintain system effectiveness through regular management reviews, performance monitoring, and adaptation to evolving EU requirements. Stay informed of regulatory updates and industry best practices.
Join auRELIA’s Pilot Program
auRELIA’s Smart HACCP Automation platform directly addresses these compliance challenges, offering Malaysian manufacturers a strategic pathway to EU market readiness. Our platform generates HACCP plans aligned with both MS1480 and EU requirements, creates comprehensive process flow diagrams, and provides AI-powered hazard analysis tools.
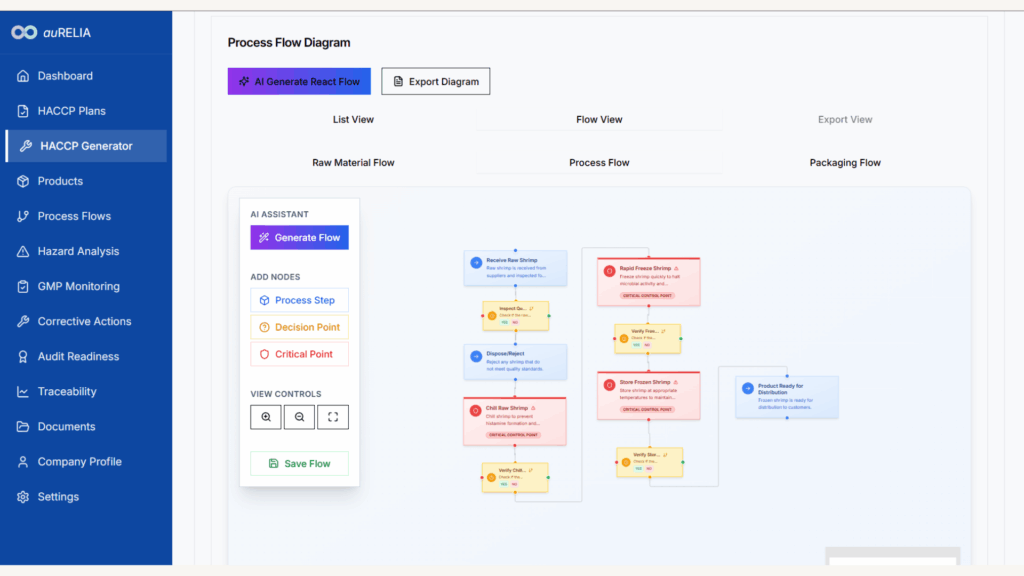
With our pilot program currently onboarding Malaysian F&B manufacturers, early adopters gain preferential access to platform features specifically designed for EU compliance preparation.
Connect With Our Founders
Ready to transform your HACCP compliance process? Connect directly with auRELIA’s leadership team:

Ms. Christin Theresa Lim, CEO
Co-founder of auRELIA Insights, specialising in food safety and regulatory compliance for Southeast Asian markets. Her expertise helps businesses navigate complex international standards and ensure seamless market access.

Mr. Arvindran Salyah, COO
Co-founder of auRELIA Insights, bringing extensive experience in market access, financial and operational advisory for agri-business, food and beverage companies. He focuses on sustainable growth and compliance efficiency.

auRELIA Insights is backed by Antler and founded by leaders driving the future of work at the intersection of people and technology. Ready to get export-ready faster? Let’s make compliance work for you—not against you.
